In my previous article, I discussed how the payments ecosystem—characterized by its high volumes, real-time processing, and rich contextual data—is naturally suited for AI. These qualities make it possible to build smarter, faster, and more reliable processes.
Building on that foundation, we’re now witnessing a new era in e-commerce, defined by the rise of autonomous transactions powered by AI agents. This concept, known as
agentic commerce, represents a major shift where AI agents act on behalf of both consumers and businesses to handle purchasing, selling, and financial operations—without direct human involvement.
In this article, I want to explore some of the most promising applications of this emerging model. We’ll look at how AI agents are reshaping both supply and demand, creating aggregation layers, and opening new opportunities for businesses ready to embrace
the next generation of commerce.
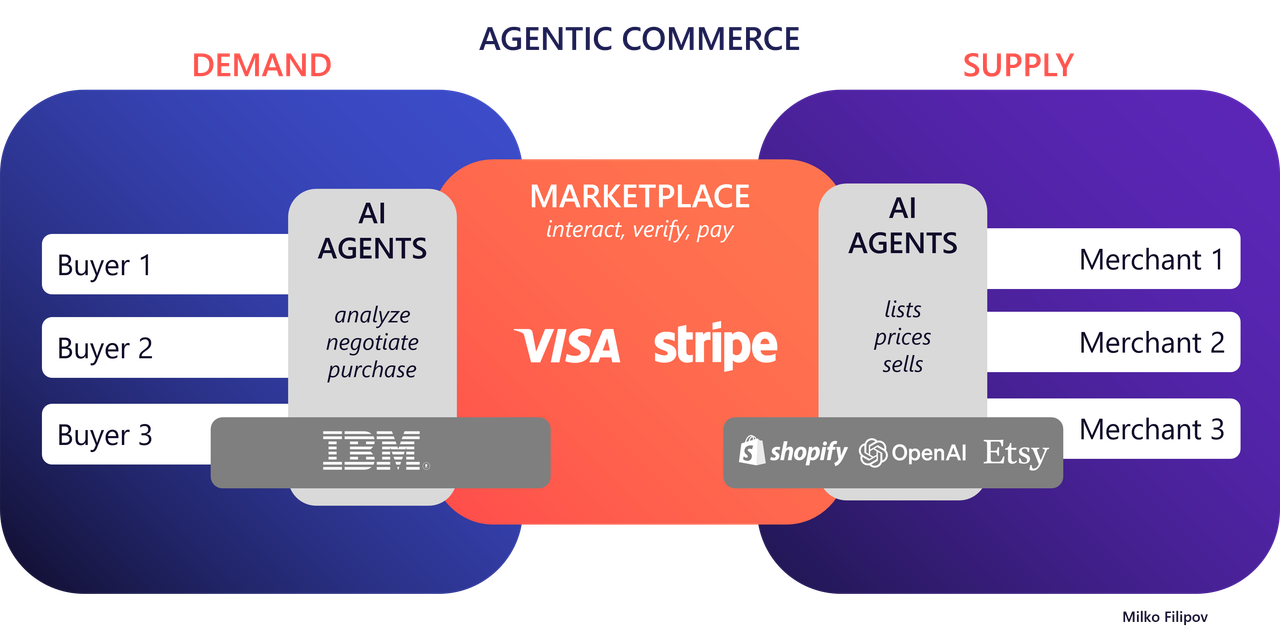
Supply Side: Enabling Autonomous Selling
On the supply side, online stores and marketplaces are evolving to support AI agents. These platforms are building systems that let AI agents autonomously list, price, and sell products or services. This evolution requires advanced APIs and standardized
protocols to ensure smooth interaction between AI agents and e-commerce platforms.
A great example is
OpenAI’s collaboration with Shopify and Etsy, which enables AI agents to browse, compare, and purchase products directly within ChatGPT conversations. Through OpenAI’s
Instant Checkout integration with these platforms, users can now browse, select, and purchase items without ever leaving the chat. Essentially, the AI agent becomes an autonomous shopper.
For merchants, this introduces a completely new sales channel and revenue stream. For consumers, it delivers a faster, more seamless shopping experience. This development highlights how AI agents are transforming e-commerce—creating
new opportunities and changing how transactions are conducted in digital marketplaces.
Demand Side: AI Agents as Autonomous Shoppers
On the demand side, companies are using AI agents to
autonomously purchase data, services, and products. These agents can analyze market trends, negotiate prices, and execute transactions—streamlining procurement processes and reducing manual effort. To make this work securely, payment systems must evolve
to handle AI-initiated transactions efficiently.
A compelling example can be found in enterprise procurement platforms
developed by IBM. These systems employ AI agents to autonomously manage tasks like supplier management, pricing, purchase order tracking, supply chain management, and market analysis. By automating these repetitive processes, AI agents free procurement
teams to focus on strategic goals—like building long-term supplier relationships and negotiating complex deals. The result is greater efficiency, lower costs, and smarter decision-making through data-driven insights.
KYC for AI Agents: Ensuring Trust and Compliance
As AI agents become active participants in transactions, trust and compliance become critical. Traditional Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are now being adapted to verify AI agents’ identities. This involves AI-driven verification systems that assess
the legitimacy of AI agents and their transactions to reduce fraud risks and ensure regulatory compliance.
One notable example is
Skyfire, which has introduced a Know Your Agent (KYA) protocol specifically for AI agents. Unlike traditional KYC that depends on human identifiers, KYA authenticates AI agents through digital credentials—such as transaction histories
and developer identities. This allows agents to prove who they are and ensures transactions remain secure and compliant. By implementing KYA, businesses can trust the agents they interact with, reduce fraud risks, and strengthen the integrity of digital commerce.
Autonomous Payments: Facilitating Secure Transactions
The rise of agentic commerce also calls for secure payment systems that can support autonomous transactions. These systems must include advanced authentication methods and real-time fraud detection to maintain transaction integrity.
Visa is one of the leaders in this area, introducing the Trusted Agent Protocol in collaboration with Cloudflare. This protocol provides a secure framework for AI agents and merchants to interact through a
cryptographic trust handshake. Each approved AI agent receives a unique digital signature key, which it uses to authenticate itself during transactions. Merchants then verify these signatures against
Visa’s registry of approved agents, ensuring that only legitimate agents can complete purchases. This approach enhances trust and security by filtering out malicious bots and protecting the ecosystem of autonomous commerce.
The Emergence of Aggregation Layers in E-Commerce
Another major development in agentic commerce is the rise of aggregation platforms that bring together offerings from various online shops and marketplaces. These serve as intermediaries, allowing users to interact with AI agents capable of browsing, comparing,
and purchasing products across multiple vendors.
OpenAI’s integration with Walmart’s Instant Checkout feature is a great illustration of this.
Walmart has partnered with OpenAI to let customers shop for groceries, apparel, and entertainment products directly through ChatGPT. Payments are handled by Stripe, and while purchases are currently limited to single items, multi-item transactions are expected
soon. Although fresh food isn’t yet included, this move aligns with consumer habits and enhances convenience—a concept Walmart aptly calls
agentic commerce.
Implications for Businesses and Merchants
The arrival of agentic commerce brings both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, it promises higher efficiency and a broader market reach. On the other, it requires significant investment in technology, infrastructure, and compliance. Businesses must
adapt by building AI-compatible platforms, staying ahead of evolving regulations, and considering the ethical implications of autonomous transactions.
In essence, the rise of agentic commerce marks a profound transformation in e-commerce. AI agents are now essential participants in enabling autonomous transactions, and companies must innovate to stay competitive in this increasingly automated world.
In my next article, I’ll explore the new protocols and frameworks that are making agentic commerce possible and shaping the future of AI-driven transactions.