[ad_1]
One significant challenge for utility service providers is the increasing complexity of managing diverse tariff structures and customer billing arrangements. Utility providers can overcome this complexity by streamlining their SAP meter-to-cash processes which can ensure accurate billing and improve customer satisfaction.
Therefore, we will explore what is SAP meter to cash process and how to manage it effectively by leveraging tools provided by SAP as well as other technologies.
| Technology | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Workload Automation (WLA) Tools | SAP workload automation provides mission critical automation for SAP meter-to-cash operations, workflows and tasks, such as data validation, invoice generation, and payment processing. | – Boosted efficiency and minimized manual intervention – Ensured smooth operations – Optimized cash flow |
| Smart Metering Technology | Automated meters with communication capabilities for remote data collection, ensuring real-time and accurate consumption tracking. | – Improved accuracy – Real-time data access – Reduced manual efforts |
| Meter Data Management (MDM) Systems | Dedicated systems for collecting, validating, and processing meter data efficiently, especially in the context of smart meter deployments. | – Efficient data processing – Accurate validation – Centralized management of meter data |
| Integration Middleware | Middleware solutions facilitating seamless data exchange and integration between different systems, ensuring end-to-end process streamlining. | – Integration of disparate systems – Real-time data exchange – Streamlined end-to-end processes |
| Billing Rules Engines | Engines automating the calculation of charges based on consumption, rates, and contractual agreements, providing flexibility in managing complex rate structures. | – Automated and accurate billing calculations – Flexibility in managing rate structures – Consistent billing processes |
| Automated Invoice Generation Processes | Automated processes within utility billing systems for efficient invoice generation, reduced errors, and improved customer billing experience. | – Efficient invoice generation – Reduced billing errors – Improved customer billing experience |
| Customer Communication Platforms | Integrated CRM systems with communication tools for automated customer engagement, timely communication, and enhanced satisfaction. | – Improved customer engagement – Timely communication – Enhanced customer satisfaction |
| Automated Payment Processing Systems | Automated systems integrated with financial modules for efficient handling of payments, accurate accounting, and streamlined revenue management. | – Efficient payment processing – Accurate financial tracking – Streamlined revenue management |
| Analytics Tools | Tools providing insights into consumption patterns, billing trends, and key performance indicators for informed decision-making. | – Informed decision-making – Proactive management based on insights – Continuous process improvement |
What is SAP meter-to-cash process?
The Meter-to-Cash (M2C) process in the context of SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) typically refers to the end-to-end business process that starts with the measurement of energy consumption (such as electricity, gas, water) by a meter and ends with the generation of an invoice for the customer.
This process is particularly relevant for any utility company and service provider who needs to bill customers based on their consumption of resources, managing cash flow efficiently and maintaining accurate documentation throughout the entire billing cycle.
Here are some key components and tools provided by SAP to handle SAP meter-to-cash process:
SAP IS-U (Industry Solution for Utilities)
SAP IS-U is a comprehensive solution designed specifically for utilities. It covers various processes, including billing, invoicing, customer service, and more. The IS-U module is a core component for managing the Meter-to-Cash process in SAP. It can integrate with SAP S/4HANA Utilities or function as a standalone solution.
- Device Management (DM): Within SAP IS-U, the Device Management module plays a crucial role in managing devices such as meters. It includes functionalities for handling meter installation, tracking meter readings, and managing device-related data.
- Billing and Invoicing: SAP provides tools for billing and invoicing within the IS-U module. This includes features for generating invoices based on meter readings, calculating charges, and handling various billing scenarios.
SAP Cloud for Utilities
SAP Cloud for Utilities is a comprehensive solution designed to enhance the meter-to-cash process in the utility industry. SAP cloud for utilities automates billing, meter data management, and customer account processes by integrating with SAP S/4HANA Utilities.
This cloud-based platform enables utilities to efficiently manage tariffs, optimize revenue collection, and gain insights through robust analytics.
SAP S/4HANA Utilities
SAP S/4HANA is an advanced enterprise resource planning (ERP) suite that integrates key business processes, providing real-time analytics and a simplified data model. In the context of utilities, SAP S/4HANA Utilities encompasses the meter-to-cash process, managing the entire lifecycle from meter reading to billing cycles.
Its unified platform supports seamless integration across utility operations, fostering a holistic approach to customer service, billing, and meter management, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and operational excellence.
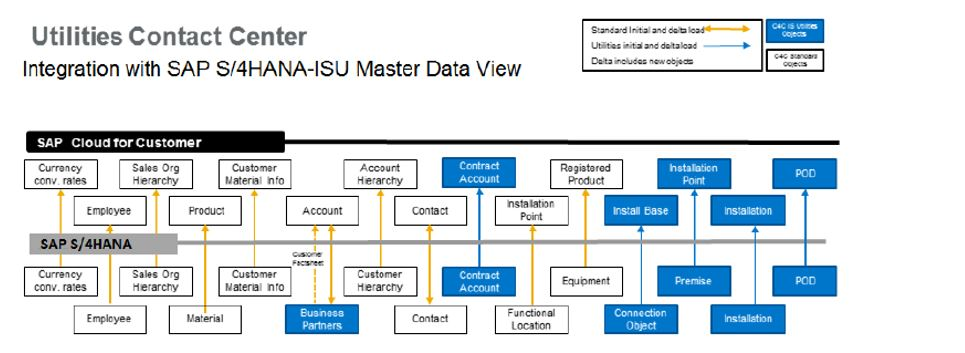
SAP Utilities Contact Center
This module enhances call center efficiency through advanced customer engagement tools tailored for sales and service processes. These capabilities seamlessly integrate with SAP IS-Utilities (IS-U), the SAP Cloud for Utilities and SAP S/4HANA, facilitating a smooth transition between various support channels. With this configuration, all utility services executed within this cloud solution are automatically reflected and updated in the Cloud for Utilities system.
SAP BW/BI
SAP Business Warehouse/Business Intelligence can be used for reporting and analytics related to the Meter-to-Cash process, providing insights into consumption patterns, billing performance, and other relevant metrics.
SAP Signavio process intelligence
SAP Signavio Process Intelligence is a tool designed to enhance visibility and understanding of business processes. With process visualization and analytics, Signavio can help in process optimization, automation, and management.
10 technologies used in SAP meter to cash process
Depending on the specific requirements of the organization, there might be integrations with external systems and solutions. Here are some major technologies and other details about their services:
1.) Workload Automation (WLA) Tools
Workload Automation (WLA) tools prove instrumental in optimizing the meter-to-cash process by automating complex workflows. WLA software can be specifically tailored for the unique demands of meter-to-cash operations, such as data validation, invoice generation, and payment processing. The substantial advantages WLA brings include:
Benefits
- Boosted efficiency and minimized manual intervention by automating entire SAP Meter-to-Cash process, from data validation to payment.
- Ensured smooth operations due to effective power distribution and monitoring.
- Optimized cash flow through automated business processes.
Explore more on SAP workload automation use cases, benefits and tools.
2.) Smart metering technology
Smart meters are equipped with communication capabilities that enable the automatic and remote collection of meter readings. They provide real-time data, reducing the need for manual readings and facilitating accurate consumption tracking.
Benefits
- Improved accuracy, real-time data access, and reduced reliance on manual processes.
- Enhanced cash flow through precise consumption data for billing.
- Streamlined documentation of meter readings for efficient record-keeping.
3.) Meter data management (MDM) systems
MDM systems are dedicated solutions that collect, validate, and process meter data. They handle large volumes of data efficiently, ensuring accuracy and providing a centralized platform for managing meter data.
Benefits
- Efficient data processing, validation, and management, especially in the context of smart meter deployments.
- Improved cash flow management with accurate and timely data processing.
- Enhanced document organization through centralized meter data management.
4.) Middleware solutions
Middleware solutions, such as process orchestration tools, can facilitate the integration of diverse systems, ensuring data flow between smart meters, MDM systems, and SAP IS-U (Industry Solution for Utilities).
Benefits
- Integration of disparate systems, real-time data exchange, and streamlined end-to-end processes.
- Improved cash flow through automated data integration for billing.
- Enhanced document flow with seamless data exchange between systems.
5.) Billing Rules Engines
Billing rules engines automate the calculation of charges based on consumption, rates, and contractual agreements. These engines are integrated with utility billing systems to ensure accurate and consistent billing.
Benefits
- Automated and accurate billing calculations, flexibility in managing complex rate structures.
- Enhanced cash flow through timely and precise billing processes.
- Improved documentation of billing rules for transparent financial transactions.
6.) Automated Invoice Generation Processes
Automated processes within utility billing systems, such as SAP IS-U, generate invoices based on the calculated charges. These processes streamline the creation and distribution of invoices to customers.
Benefits
- Efficient invoice generation, reduced billing errors, and improved customer billing experience.
- Accelerated cash flow through automated and timely invoice generation.
- Enhanced document generation for organized billing records.
7.) Automated Payment Processing Systems
Automated systems for payment processing are integrated with financial modules to handle payments received from customers. These systems ensure accurate accounting and reconciliation of payments.
Benefits
- Efficient payment processing, accurate financial tracking, and streamlined revenue management.
- Improved cash flow through automated and error-free payment processing.
- Organized documentation of financial transactions for audit purposes.
8.) Analytics Tools
Analytics tools provide insights into consumption patterns, billing trends, and key performance indicators. These tools support data-driven decision-making and strategic planning.
Benefits
- Informed decision-making, proactive management based on insights, and continuous process improvement.
- Enhanced cash flow forecasting through data-driven insights.
- Improved documentation of analytics results for future planning.
9.) Monitoring Tools
Monitoring tools, such as CCMS, keep track of the performance of automated processes. They provide alerts and reports, enabling utilities to identify and address issues promptly.
Benefits
- Continuous process monitoring, early issue detection, and improved system reliability.
- Enhanced cash flow management through proactive issue resolution.
- Documented records of system performance for future optimizations.
10.) Process intelligence tools
Process intelligence tools such as task mining, process mining or DTO analyze event logs data to deliver actionable insights on operations, tasks and processes. These tools can integrate to IT systems and various applications, including SAP.
Benefits
- Real-life insights and interactive process maps to understand meter to cash process better
- Automatically generated root cause analysis for detected issues and variations
- Alerts and continuous monitoring for potential problems.
Explore how to use process mining in utility industry.
What is meter to cash process?
The Meter-to-Cash process is a generic term that broadly describes the end-to-end workflow in utility services, covering activities from measuring energy consumption to billing and payment. It encompasses activities from measuring and recording energy consumption through utility meters to generating bills and receiving payment from customers. This process involves the accurate metering of energy usage, billing based on consumption, and managing financial transactions related to customer accounts.
Why is it important to improve SAP meter to cash process?
Automating and improving SAP meter to cash process can lead to:
– Enhanced efficiency: SAP Meter-to-Cash streamlines the entire workflow, reducing manual efforts and enhancing operational efficiency.
– Increased accuracy: The automation and integration features ensure accurate meter readings, billing calculations, and financial transactions, minimizing errors.
– Achieved billing transparency: Customers gain transparency into their energy consumption and billing details, fostering trust and satisfaction.
– Streamlined financial management: The process supports effective financial management, providing utilities with insights into revenue streams and financial performance.
– Easy regulatory compliance: SAP solutions often incorporate features to ensure compliance with industry regulations, helping utilities meet legal requirements.
– Facilitated data Integration: SAP Meter-to-Cash facilitates seamless integration with other enterprise systems, enabling a holistic view of utility operations.
– Improved customer satisfaction: By improving billing accuracy, transparency, and overall service, SAP Meter-to-Cash contributes to higher customer satisfaction levels.
– More operational insights: The data generated and processed during the Meter-to-Cash process can be leveraged for analytics, offering utilities valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Further reading
Learn more on top technologies that transform utility companies by checking out articles on:
If you need more help regarding SAP meter to cash process, let us:
Find the Right Vendors
External links
- Jha, C. (2020) “SAP C4C integration with S4/Hana Utility Series- Part 1-Introduction and Architecture.” SAP. Accessed at January 11, 2024.
Source link
