[ad_1]
According to estimates, more than 500 million apps have been created between 2018-2023. The latest software development stats show that:
These trends are changing software development projects considering quality and maintainability. Also, IDE platforms pave the way to resource coordination and team communication issues as project developers, testers and managers work in different countries and time zones.
Process mining can overcome these challenges by monitoring projects, assessing compliance issues and identifying areas for further improvement. The latest academic studies show that 75% of papers that study process mining applications in software development were published in the last 3 years, implying increasing interest over the previous few years. 1 Yet, the number of business applications remains limited.
Therefore, this article explains process mining software development use cases, real-life examples, and benefits in detail to help business leaders, project managers, and software developers implement process intelligence.
7 process mining software development use cases
The way process mining extracts data from software systems and analyze it via process discovery, conformance checking and enhancement is illustrated in Figure 1. Process mining delivers insights that help software developers and project managers improve quality, optimize processes and increase efficiency.
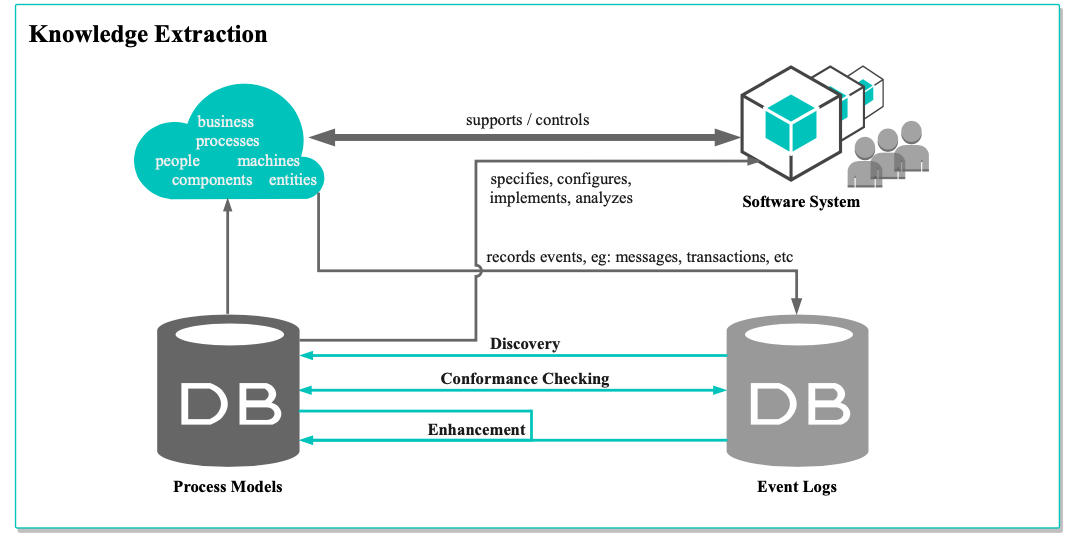
Some process mining use cases in software development include:
1.Tracking the life cycle activities
The software development life cycle (SDLC) refers to the required stages while developing software (See Figure 2). SDLC offers an effective framework and method to
- Plan development project
- Analyze requirements
- Minimize costs
- Predict mistakes
- Design and build high-quality products
- Test and evaluate the software.

Process mining can help track the entire software development life cycle by discovering and mapping the actual process model. This way, developers and project managers can identify if any steps are skipped.
2. Monitoring and managing software projects
Typically, a development project takes around 2 to 12 months. 3 Software project managers are expected to monitor project progress and risks, identify bottlenecks and manage quality, cost, schedule and communication during this time. However, monitoring and managing the entire project can be challenging, given the time constraints.
Process mining can map the entire project flow, allowing every party in the software development team to monitor and manage the project while identifying issues and risky areas. Also, process mining illustrates process KPIs (e.g., cost and time), resources and parties involved in the given process.
For example, a BPM software provider company in Australia applied process mining to manage their customer project journey. With the help of process mining, the firm identified and solved compliance and performance problems. 4
3. Quality Assurance
Software development focuses on delivering high-quality software in the shortest time possible. Yet, 49% of software development projects were reported as failing. 5
QAs control for software’s usability, accuracy, maintainability and portability. QA includes quality control and several testing, such as:
- Usability test
- Design test
- Integration test
- Unit test
Process mining offers conformance checks and automated root cause analysis, which can help testers to complete QA easily and ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of the QA process.
4. Ensure compliance
Process mining conformance checks can assess the compliance level against rules, regulations and standards. This way, software providers can monitor and intervene when the product does not meet the requirements.
In a case study, researchers deployed process mining in a software development process dataset provided by a Brazilian software house with more than 2000 cases (See Figure 3). In their conformance analysis, researchers pointed out that:
- 90% of the cases follow the order of execution defined in the formal process
- 25% of the processes skipped the planning stage
- 43.6% of projects were neither tested nor documented. 6

5. Assess performance
Process mining offers customizable dashboards and process KPIs. Software development managers can use these metrics to assess the performance of the tool, project and developers and testers.
In a case study, researchers applied process mining to software development processes (See Figure 4) and identified that:
- 3 users in the support team were responsible for reworking items the most
- The analysis step in the model was skipped in real applications
- 50% of entities for which an analysis is not performed a required reworking. 7
As a result, researchers advised additional training for three users. They introduced analysis as a mandatory step to verify requirements, definitions and user engagement.

6. Incident Management
Incident management is a process to address and correct any unplanned activity that may reduce service quality and operations. Successful incident management is essential to maintain normal service and minimize costs.
Process mining can improve incident management and resolution processes by discovering automation and further optimization opportunities. Predictive process mining and monitoring capabilities can allow developers, testers and managers to forecast potential incidents and intervene in time.
7. Allocate and coordinate resources
Resource coordination is one of the fundamental issues in software development due to the complexity of teams’ behaviors and dependencies between tasks.
Process mining generates process visuals based on people and resources, allowing project managers to view teams’ activities and how resources are allocated among tasks. By understanding complicated relationships, project managers can easily coordinate their teams and resources and re-allocate them if needed.
6 Benefits of deploying process mining in software development
Process mining provides several benefits in software development, including:
- Improving process efficiency by identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies to optimize their processes and reduce waste.
- Increasing transparency by providing a clear and comprehensive view of the software development processes.
- Enhancing decision-making about process improvements and resource allocation by enabling organizations.
- Enabling collaboration between teams and departments by providing a common understanding of the software development process.
- Aligning with business objectives by allowing them to prioritize work and allocate resources more effectively.
- Boosting quality of products and services by identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks in the software development process.
3 Challenges of using process mining for software development
The use of process mining in software development presents several challenges, including:
- Data availability and quality: Ensuring that the right and quality data is a challenge in software development process mining. This data may come from multiple sources, such as source code repositories, issue trackers, and log files complicating data quality and consistency.
- Technical complexity: Implementing process mining in software development can be technically complex, requiring knowledge of the software development process and the tools used to extract and analyze data.
- Integration with existing tools: Integrating process mining tools with existing software development tools, such as issue trackers and project management systems, can be difficult, especially if these tools are custom-built.
Further reading
Explore more on process mining applications and case studies in other fields:
Download our whitepaper for free to learn more on process mining:
Explore Process Mining
If you believe you can improve your software development projects with the help of process mining, start comparing tools through our data-driven and comprehensive vendor lists.
Assess different vendors with a transparent methodology yourself by downloading our checklist:
Get Process Mining Vendor Selection Guide
If you need more help, let us know:
Find the Right Vendors
- Caldeira, J., & e Abreu, F. B. (2016, September). “Software development process mining: Discovery, conformance checking and enhancement.” In 2016 10th International Conference on the Quality of Information and Communications Technology (QUATIC) (pp. 254-259). IEEE. Revisited March 23, 2023.
- “Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).” Bigwater Consulting. 2019. Revisited March 23, 2023.
- “Modernization: Clearing a Pathway to Success.” StandishGroup. Revisited March 23, 2023.
- Process Mining: a database of applications. HSPI. 2021. Revisited March 23, 2023.
- “Modernization: Clearing a Pathway to Success.” StandishGroup. Revisited March 23, 2023.
- Lemos, A. M., Sabino, C. C., Lima, R. M., & Oliveira, C. A. (2011, October). “Using process mining in software development process management: A case study.” In 2011 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (pp. 1181-1186). IEEE. Revisited March 23, 2023.
- Sebu, M. L., & Ciocarlie, H. (2014, May). “Applied process mining in software development.” In 2014 ieee 9th ieee international symposium on applied computational intelligence and informatics (saci) (pp. 55-60). IEEE. Revisited March 23, 2023.
Source link

